Operation Modes for Mach5 Ingestion
This document details the modes in which we can ingest data into Mach5. These three modes are Append, Upsert and Update. The Ingest Pipeline - Advanced options need to be configured to choose one of the three modes for ingestion. Default is Append/Upsert
Prerequisites
- This document assumes that Mach5 is deployed and running successfully. Mach5 Administrative UI page looks as below. Let’s assume it’s running at http://localhost:8888/
- Store, store route and warehouse are created successfully in Mach5. Refer to Quickstart document for help
- This document considers the data source as Kafka.
- There is a Mach5 Connection kafkaconn of type Kafka created. Refer to documentation here for more information regarding configuration of connection and ingest pipelines with Kafka
Operation Modes
Every record that is ingested into Mach5 is identified by a unique field _id. This is either auto generated by Mach5 or user specified at the time of ingestion. For Append mode, Mach5 generates the _id. For Upsert and Update to work, records should have the user specified unique _id during ingestion.
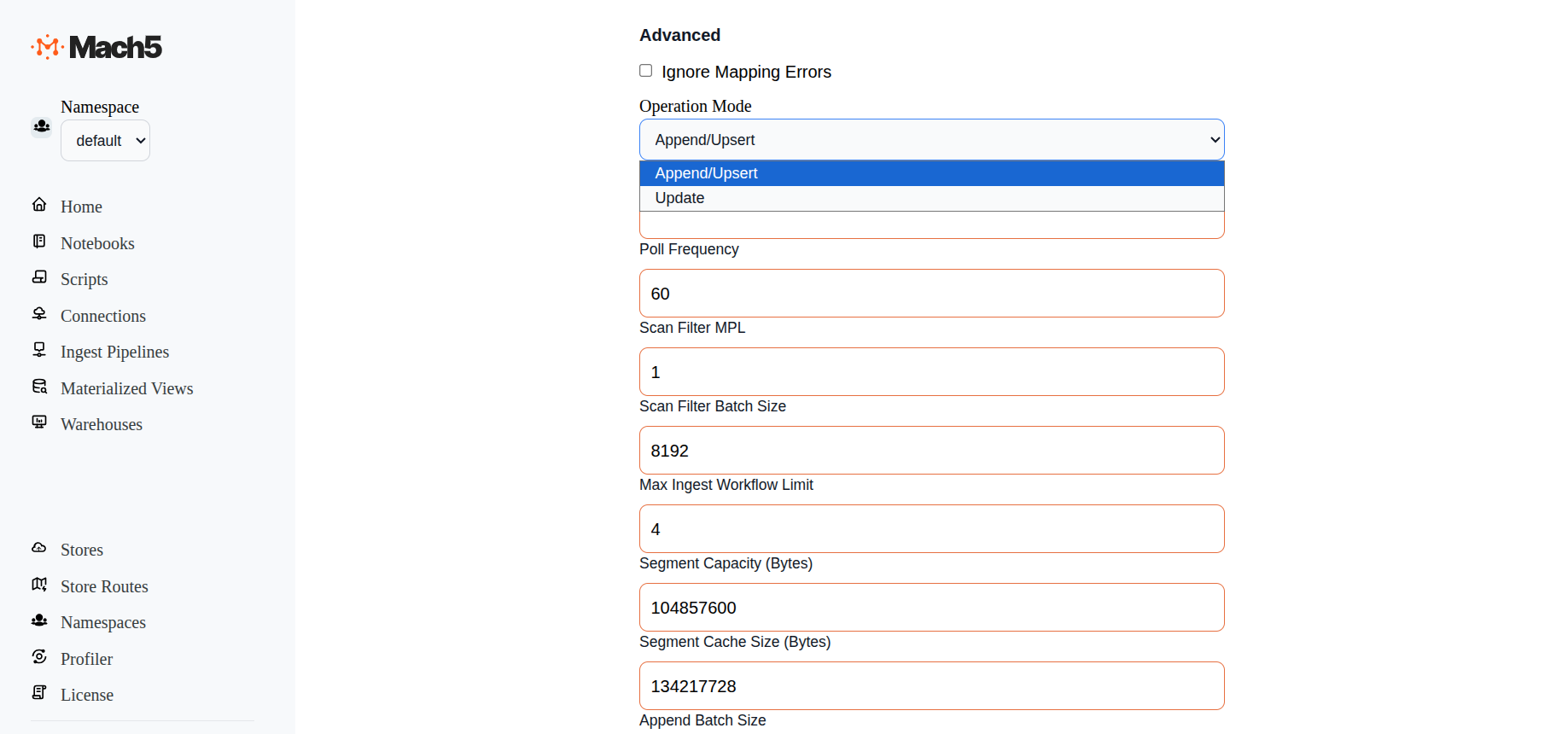
Note: When creating an Ingest Pipeline, Append and Upsert modes appear the same from a user perspective, so the default option is Append/Upsert. Internally, Mach5 determines the behaviour based on whether the incoming data includes an _id field: If _id is present: Mach5 performs an Upsert, replacing the existing document if it exists or inserting a new one if it doesn’t. If _id is absent: Mach5 performs an Append, always inserting a new document. The Update mode, on the other hand, specifically modifies existing documents without inserting new ones. It requires that the incoming records include an _id value corresponding to existing documents in the index. If a matching document is not found, no new record is created.
Append/Upsert Mode
This is the default mode of operation for Mach5, Append/Upsert mode. Let’s understand the concept details with examples.
Append
Consider that a user wants to add new records in Mach5. Append mode adds new records to the Mach5 index without checking for or modifying existing entries. For each record that is ingested into Mach5 a unique _id is generated for it. When an Ingest Pipeline is created for any type of data source, default in Advanced option for Operation Mode is Append/Upsert. Whenever any ingestion takes place and records do not have _id in them, Append mode of operation path for ingestion is taken
Upsert
Consider that a user wants to replace an existing record in Mach5. Upsert mode verifies the existence of a document; if found, the existing document is fully replaced with the new record, otherwise a new document is inserted. Requirement is that records should have user specified or system generated _id in them.
User specifies records with _id for which upsert needs to happen. In Mach5 upsert is implemented as a complete replacement of the existing record with given _id.
- If the record with _id exists at the time of ingestion, then the current record with existing _id is deleted and a new record with _id is added.
- If the record with _id does not exist in Mach5, new record is added with that _id
Prerequisites
- Let’s consider that Mach5 has an index named append-upsertindex
- Let’s also consider that Kafka is configured and append-upserttopic has following data enqueued on that topic: 3 records have user defined _ids. 1 record is not assigned user defined _id
{"_id": "10001", "id": "1", "value" : "111"}
{"_id": "10002", "id": "2", "value" : "222"}
{"_id": "10003", "id": "3", "value" : "333"}
{"id": "4", "value" : "444"}
- Create an Ingest Pipeline kafka-append-upsert-ip of type Kafka and using kafkaconn connection
- Let the Advanced Mode of Operation be default - Append/Upsert.
- After Ingest Pipeline is saved, 4 records from append-upserttopic are ingested into append-upsertindex
Initial Records in Mach5 index (Append/Upsert)
After the kafka data is inserted into Mach5 index, example of a record in the Mach5 index append-upsertindex. 3 records that are ingested have user defined _ids and 1 record will have system generated _id
{ "_index" : "upsertindex",
"_id" : "10001",
"_source" : {
"id" : "1",
"value" : "111"
}
"_id" : "10002",
"_source" : {
"id" : "2",
"value" : "222"
}
"_id" : "10003",
"_source" : {
"id" : "3",
"value" : "333"
}
"_id" : "cedbf3ca-7de3-4271-891a-e648f200c05f",
"_source" : {
"id" : "4",
"value" : "444"
}
}
Append/Upsert additional records
Consider the following example of records for Append and Upsert in Kafka. This is how they should appear as a message enqueued on the Kafka append-upserttopic:
There are 4 different flavors for append/upsert record examples:
- Add a record (Upsert) with existing user defined _id i.e. 10002
- Add a record (Upsert) with existing system generated _id i.e. “cedbf3ca-7de3-4271-891a-e648f200c05f”
- Add a record (Append) with non-existing _id
- Add a record (Upsert) with same existing user defined _id i.e. 10002 (note _id with 10002 is added twice)
{"_id": "10002", "id": "2", "value" : "99999"}
{"_id": "cedbf3ca-7de3-4271-891a-e648f200c05f", "id": "4", "value" : "99999"}
{"_id": "10005", "id": "5", "value" : "555"}
{"_id": "10002", "id": "2", "value" : "77777777"}
Additional Records in Mach5 Index (after Append/Upsert)
Mach5 records would look like following after an Append/Upsert operation in append-upsertindex
-
The existing record with _id 10002 is completely first replaced by record with value 99999. After last Kafka record is inserted with _id 10002, the existing record with _id 10002 is again replaced completely by record with final value as 77777777.
Note: Kafka - In Kafka as the records are in a definite order, the ingestion in Mach5 Index guarantees same order. Especially for same _id records the order for upsert is guaranteed when data source is Kafka. When using a multi-partitioned topic, the partition key must include the _id field to guarantee that events for the same record are processed in the correct order.
Note: S3 - If multiple records with the same _id are upserted from an S3 data source ingest-pipeline, Mach5 does not guarantee which version will be retained in the index.
-
The value of existing record with auto generated _id “cedbf3ca-7de3-4271-891a-e648f200c05f” is completely replaced by record with value 99999 and same _id
-
As the _id with 10005 values is not found in append-upsertindex, this record gets newly added/appended in the index
{ "_index" : "append-upsertindex",
"_id" : "10001",
"_source" : {
"id" : "1",
"value" : "111"
}
"_id" : "10002",
"_source" : {
"id" : "2",
"value" : "77777777"
}
"_id" : "10003",
"_source" : {
"id" : "3",
"value" : "333"
}
"_id" : "cedbf3ca-7de3-4271-891a-e648f200c05f",
"_source" : {
"id" : "4",
"value" : "99999"
}
"_id" : "10005",
"_source" : {
"id" : "5",
"value" : "555"
}
}
Update Mode
In Mach5, Update mode of operation is different from Append/Upsert mode as below:
Consider that a user wants to update some specific fields of an already existing record in Mach5, not the entire record data. Update mode modifies specific fields of an existing record based on the _id field.
User specifies a record with _id and details for updates using VRL script, Mach5 does the following:
- Retrieves the record with _id, if it exists
- Applies the specified updates, which may include:
- Modifying existing field values
- Adding new fields
- Deleting existing fields
- Performing no operation (noop)
- The updated record is stored back for that existing _id
- If the record with _id does not exist in Mach5, it is a noop case
This section outlines the complete flow regarding how to specify updates to existing records using VRL scripts.
Prerequisites
- Let’s consider that Mach5 has an index named updateindex
- Let’s also consider that Kafka is configured and updatetopic has data enqueued on it
- Create an Ingest Pipeline kafka-update-ip of type Kafka and using kafkaconn connection
- Select the Advance Mode of Operation as Update
- After Ingest Pipeline is saved, 1 record from updatetopic is ingested into updateindex
Example record in the Mach5 index (Update)
Here’s an example of an existing record in the Mach5 updateindex:
{"_index" : "updateindex",
"_id" : "doc-00000001",
"_source" : {
"extra" : {
"source_key" : ["old_key"]
},
"version" : 1
}
}
Expected updated record (after Update)
Let’s say we need the example record ingested in Mach5 updateindex to look like below after updates are done to it:
- New source key is appended in source_key field. Old key is kept intact
- A new field last_update specifies the last updated time
- version is changed to -1
{"_index" : "updateindex",
"_id" : "doc-00000001",
"_source" : {
"extra" : {
"last_update" : "2023-10-16T15:58:01.0000000",
"source_key" : ["old_00000001", "nb_00000001"]},
"version" : -1
}
}
Example update record structure
To achieve the updates shown above in existing Mach5 record, following steps need to be taken:
- An update record needs to be created to specify the updates needed.
- Mach5 supports VRL script to specify the udpates to be performed. Update record should have that VRL script
- This update record then needs to be enqueued in Kafka.
- When ingesting such an update record, Mach5 performs the needed updates as specified in the VRL script.
Let’s take an example update record structure to understand the above flow:
{ "_id": "doc-00000001",
"script": {
"lang": "vrl",
"params": {
"new_breach_id": "new_key",
"last_update": "new_updated"},
"source": "if !is_array(.ctx._source.extra.source_key)
{\n return null \n}
\n .ctx._source.extra.source_key = array!(.ctx._source.extra.source_key) \n
if !(includes(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id))
{\n .ctx._source.extra.source_key = push(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id)
\n .ctx._source.extra.last_update = .params.last_update\n}
else
{\n .ctx.op = "noop"\n}"
}
}
Note: The above message should be present in a single line on the kafka topic.
- _id: The _id of the record for which the update needs to be performed
- script has following fields:
- lang: Mach5 currently supports VRL script only
- params: Parameters to the script for updating the record
- source: VRL script source
.ctx object
Mach5 provides a .ctx object automatically to the VRL script and has the following structure:
ctx: {
op: "index",
now: _now,
_id: id,
_source: value }
- The op field indicates the operation to be performed. It can be one of index, noop or delete.
- Operation index means that if the document with the given _id exists, it will be updated.
- Operation noop means that no changes are made to the index; the record is ignored.
- Operation delete means that the document with the given _id will be deleted if it exists.
Reference
VRL script explanation
if !is_array(.ctx._source.extra.source_key) {\n return null \n}
\n .ctx._source.extra.source_key = array!(.ctx._source.extra.source_key) \n
if !(includes(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id))
{\n .ctx._source.extra.source_key = push(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id)
\n .ctx._source.extra.last_update = .params.last_update\n}
else
{\n .ctx.op = "noop"\n}
Let’s understand what the VRL script in update of record does:
if !is_array(.ctx._source.extra.source_key) {return null}
- If .ctx._source.extra.source_key is not an array, stop (return null).
.ctx._source.extra.source_key = array!(.ctx._source.extra.source_key)
- Converts the field into an array (even if it was a single value)
- Example: “id1” → [“id1”]
if !(includes(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id))
- includes(array, value) → true if array contains the value
- !(…) → means “if NOT included”
{.ctx._source.extra.source_key = push(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id)\n
.ctx._source.extra.last_update = .params.last_update}
else { .ctx.op = "noop” }
- Adds (push) the new breach ID into the array
- Updates the last_update field with .params.last_update
- If the breach ID was already there → no update required
- Setting .ctx.op = “noop” tells the system to skip updating the record
How to test in VRL playground
The VRL Playground is a helpful tool to test and debug VRL scripts interactively. Here’s a step-by-step guide to use it with your given script and event:
Copy the Script
Paste the following VRL script into the Script section:
if !is_array(.ctx._source.extra.source_key) { return null }
.ctx._source.extra.source_key = array!(.ctx._source.extra.source_key)
if !(includes(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id))
{.ctx._source.extra.source_key = push(.ctx._source.extra.source_key, .params.new_breach_id)
.ctx._source.extra.last_update = .params.last_update}
else {.ctx.op = "noop"}
Provide the Event Input
In the Event (Input) section, paste the following event data:
{
"ctx": {
"op": "index",
"_source": {
"extra": {
"source_key": ["old_key"]},
"version": 1 }
},
"params": {
"new_breach_id": "new_key",
"last_update": "new_updated" }
}
Run and Observe the Output
When you run the script in the VRL Playground, you should get the following output:
{"ctx": {
"_source": {
"extra": {
"last_update": "new_updated",
"source_key": ["old_key","new_key"] },
"version": 1},
"op": "index" },
"params": {
"last_update": "new_updated",
"new_breach_id": "new_key"}
}
This means:
- The script identified that “new_key” was not already present in source_key.
- It appended the new key and updated the last_update field.
- Since a change was made, the operation remained “index” (not “noop”)